Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sc
Sc O
O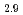
Shimoyama, Tomotaka*; Tojo, Takeo*; Kawaji, Hitoshi*; Atake, Toru*; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Igawa, Naoki
Solid State Ionics, 180(6-8), p.560 - 562, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.44(Chemistry, Physical)The neutron diffraction of BaZr Sc
Sc O
O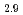 with and without proton were measured and analyzed by Rietveld method and Maximum Entropy Method. We found that the location of proton is 12
with and without proton were measured and analyzed by Rietveld method and Maximum Entropy Method. We found that the location of proton is 12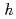 site near oxygen ion. The heat capacity of sample with proton is larger than that without proton. This difference is discussed in term of the changes of the crystal structure and lattice vibrations due to the dissolution of proton.
site near oxygen ion. The heat capacity of sample with proton is larger than that without proton. This difference is discussed in term of the changes of the crystal structure and lattice vibrations due to the dissolution of proton.
Xianglian*; Siagian, S.*; Basar, K.*; Sakuma, Takashi*; Takahashi, Haruyuki*; Igawa, Naoki; Ishii, Yoshinobu*
Solid State Ionics, 180(6-8), p.480 - 482, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.75(Chemistry, Physical)Correlation effects among thermal vibrations of atoms are very important to realize the thermal properties of materials. We discuss the inter-atomic distance and temperature dependence of the correlation effects in ionic crystal, AgBr, CuBr, CuI and CuCl, by neutron diffraction method. From the Rietveld analysis of those diffraction data the lattice constants and Deby-Waller parameters were determined. The diffuse scattering of diffraction data was analyzed with the correlation effect,  . It is found that the
. It is found that the  is 0.6-0.75 for the inter-atomic distance around 2.5
is 0.6-0.75 for the inter-atomic distance around 2.5 and 0.4-0.5 for 4
and 0.4-0.5 for 4 for all ionic crystals. The value of
for all ionic crystals. The value of  decreases with the decrease of temperature.
decreases with the decrease of temperature.
 O
O
Basar, K.*; Xianglian*; Sainer, S.*; Ohara, Kota*; Sakuma, Takashi*; Takahashi, Haruyuki*; Abe, Osami*; Igawa, Naoki; Ishii, Yoshinobu*
no journal, ,
Lithium-based metal oxides are promising for next generation of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. LiMn O
O studied as a cathode for those batteries because it is relatively cheap and save. Powder of LiMn
studied as a cathode for those batteries because it is relatively cheap and save. Powder of LiMn O
O was prepared by solid state reaction of LiOH and MnO
was prepared by solid state reaction of LiOH and MnO . The crystallite size was analyzed from neutron diffraction patterns using Scherrer equation and the conductivity was measured by DC method. The anneal temperature effect on the crystallite size and conductivity is discussed.
. The crystallite size was analyzed from neutron diffraction patterns using Scherrer equation and the conductivity was measured by DC method. The anneal temperature effect on the crystallite size and conductivity is discussed.
Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kartini, E.*
no journal, ,
In order to elucidate the universal mechanism of high ionic conductivity in superionic conducting materials, the comparison of dynamical properties at low-energy region between superionic phase and insulator phase should significantly contribute to our understandings. The detailed investigation of Q-dependence at low-energy region made clear that an excess intensity at around Q=2.2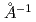 is characteristic of Ag-based superionic materials, irrespective of structural periodicity. Furthermore, we found the clear correlation between dc ionic conductivity and integrated intensity at low-energy region. These features suggest the universality of high ionic conductivity mechanism of superionic conducting materials.
is characteristic of Ag-based superionic materials, irrespective of structural periodicity. Furthermore, we found the clear correlation between dc ionic conductivity and integrated intensity at low-energy region. These features suggest the universality of high ionic conductivity mechanism of superionic conducting materials.